Products >> Herbicides >> Oxadiazon
Oxadiazon
Oxadiazon 95%TC
Oxadiazon 40%SC
Oxadiazon 50%WDG
Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; oxadiazole
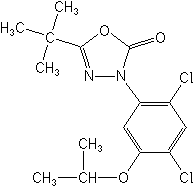
Oxadiazon NOMENCLATURE
Common name oxadiazon (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF)
IUPAC name 5-tert-butyl-3-(2,4-dichloro-5-isopropoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[2,4-dichloro-5-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl]-5-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one
CAS RN [19666-30-9] EEC no. 243-215-7 Development codes 17 623 RP
Oxadiazon APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action
Selective contact herbicide. Uses Pre-emergence control of bindweed,
annual broad-leaved weeds and grasses, and post-emergence control
of bindweed and annual broad-leaved weeds, in carnations, gladioli,
roses, fruit trees and bushes (including citrus), vines, ornamental
trees and shrubs, hops, cotton,rice, soya beans, sunflowers, onions,
and turf. Effective against mono- and dicotyledonous weeds in rice,
at c. 1 kg/ha; in orchards and vineyards, at 2 kg/ha post-em. or
4 kg/ha pre-em. Phytotoxicity Carnations are tolerant of over-the-top,
post-emergence application. Not to be used on red fescue, bentgrass
turf, dichronda or centipedegrass. Formulation types AL; EC; GR;
SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Ronstar' (Aventis)
Oxadiazon OTHER TRADENAMES
'Foresite' (Aventis); 'Explorer' (Rocca); 'Herbstar' (Vapco); 'Oryza'
(Tecomag) Discontinued names mixtures: 'Delcut' * (+ butachlor)
(Hokko)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (J. Desmoras et al., Anal. Methods Pestic.
Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 595). Residues determined by glc (idem,
ibid.). Other glc and hplc methods available from Aventis.
Oxadiazon MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute
percutaneous LD50 for rats and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Slightly
irritating to eyes; negligible irritant to skin (rabbits). Inhalation
LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.77 mg/l. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats
and mice receiving 10 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. Toxicity
class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) IV EC hazard N;
R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (24 d) for mallard ducks >1000, bobwhite
quail >2150 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout and bluegill
sunfish 1.2 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >2.4 mg/l. Algae EC50 6-3000
mg/l. Bees LD50 >400 mg/bee, with repellent effect. Mortality
is negligible by direct contact at doses up to 27 kg a.i./ha. Worms
Not toxic at recommended rate.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 93% is eliminated
within 72 hours, predominantly in the urine. Plants Oxadiazon penetrates
plants primarily via shoots and leaves and is rapidly metabolised.
Metabolites do not accumulate in the plant. Soil/Environment Strongly
adsorbed by soil colloids and humus, with very little migration
or leaching. Negligible loss due to volatilisation. Half-life in
soil is c. 3-6 mo. See D. Ambrosi et al., J. Agric. Food Chem.,
1977, 25, 868. Koc 1400 (silt loam) to 3200 (sand) at 25