Products >> Herbicides >> Metribuzin
Metribuzin
Metribuzin 95%TC
Metribuzin 70%WG
Metribuzin 70%WP
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,2,4-triazinone
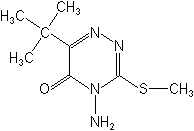
NOMENCLATURE
Common name metribuzin (BSI, E-ISO, WSSA); metribuzine ((f) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 4-amino-6-tert-butyl-4,5-dihydro-3-methylthio-1,2,4-triazin-5-one;
4-amino-6-tert-butyl-3-methylthio-1,2,4-triazin-5(4H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name 4-amino-6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-(methylthio)-1,2,4-triazin-5(4H)-one
CAS RN [21087-64-9] EEC no. 244-209-7 Development codes Bayer 94
337; DIC 1468 (both Bayer); DPX-G2504 (Du Pont)
Metribuzin APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the
photosystem II receptor site. Selectivity is due to metabolism (mostly
conjugation) within the plant (C. Fedtke, Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf.
- Weeds, 1993, 1,221). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide,
absorbed predominantly by the roots, but also by the leaves, with
translocation acropetally in the xylem. Uses Pre- and post-emergence
control of many grasses and broad-leaved weeds in soya beans, potatoes,
tomatoes, sugar cane, alfalfa, asparagus, maize and cereals, at
0.07-1.05 kg a.i./ha. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many crops, including
crucifers, cucurbits, lettuce, onions, sugar beet, sunflowers, flax,
strawberries, sweet potatoes, and tobacco. Formulation types SC;
WG; WP. Compatibility Compatible with most other herbicides, except
in highly concentrated mixtures. Selected tradenames: 'Lexone' (Du
Pont); 'Sencor' (Bayer); 'Mistral' (Feinchemie Schwebda); mixtures:
'Axiom' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer)
Metribuzin OTHER TRADENAMES
'Sencoral' (in France) (Bayer); 'Sencorex' (in Great Britain) (Bayer);
'Citation' (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'Feinzin' (Feinchemie Schwebda);
'Major' (Crop Health); 'Metiroc' (Rocca); 'Pataprop' (Hermoo); 'Premercas'
(CAS); 'Qingcaotong' (Shenzhen Jiangshan); 'Vapcor' (Vapco) mixtures:
'Artist' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer); 'Axiom AT' (+ atrazine+ flufenacet)
(Bayer); 'Bastille' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer); 'Canopy' (+ chlorimuron-ethyl)
(Du Pont); 'Domain' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer); 'Fedor' (+ flufenacet)
(Bayer); 'Galice' (+ amidosulfuron) (Bayer); 'Pilar' (+ rimsulfuron)
(Du Pont); 'Plateen' (+ flufenacet) (Bayer); 'Preview' (+ chlorimuron-ethyl)
(Du Pont); 'Salute' (+ trifluralin) (Bayer); 'Segal' (+ amidosulfuron)
(Bayer) Discontinued names mixtures: 'Turbo' * (+ metolachlor) (Bayer,
Novartis)
Metribuzin ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (AOAC Methods, 1995, 984.11; CIPAC
Handbook, 1988, 1D, 124) or by i.r. spectrometry (J. W. Betker et
al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1976, 59, 278). Residues determined
by glc (C. A. Anderson, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul.,
1976, 8, 453). In drinking water, by gc with FID (AOAC Methods,
1995, 991.07). Details available from Bayer AG.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Metribuzin
Reviews Toxikologie der Herbizide, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
[Data collection on toxicology of herbicides], 7. Lieferung, Weinheim,
1981. Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 2000, mice c. 700, guinea
pigs c. 250, cats >500 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for rats >20 000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin and eyes
(rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.65 mg/l air (dust).
NOEL (2 y) for rats and dogs 100, mice c. 800 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.013
mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation)
III EC hazard Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 168, mallard ducks 460-680
mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >4000
mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 80, rainbow trout
76, goldfish >10, catfish >10 ppm. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 4.5-35
mg/l. Algae ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.021 mg/l. Bees Not
toxic to bees; LD50 35 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida 331.8
mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 98% elimination
occurs within 96 hours, about equally in the urine and the faeces.
Plants In plants, metribuzin undergoes oxidative deamination and
further degradation to water-soluble conjugates. Soil/Environment
Metribuzin is rapidly degraded in soil; microbial breakdown is the
major mechanism of loss. Degradation involves deamination, followed
by further degradation to water-soluble conjugates. Photodecomposition
on soil surfaces and in aqueous solution is an important process
for the degradation of metribuzin in the environment.